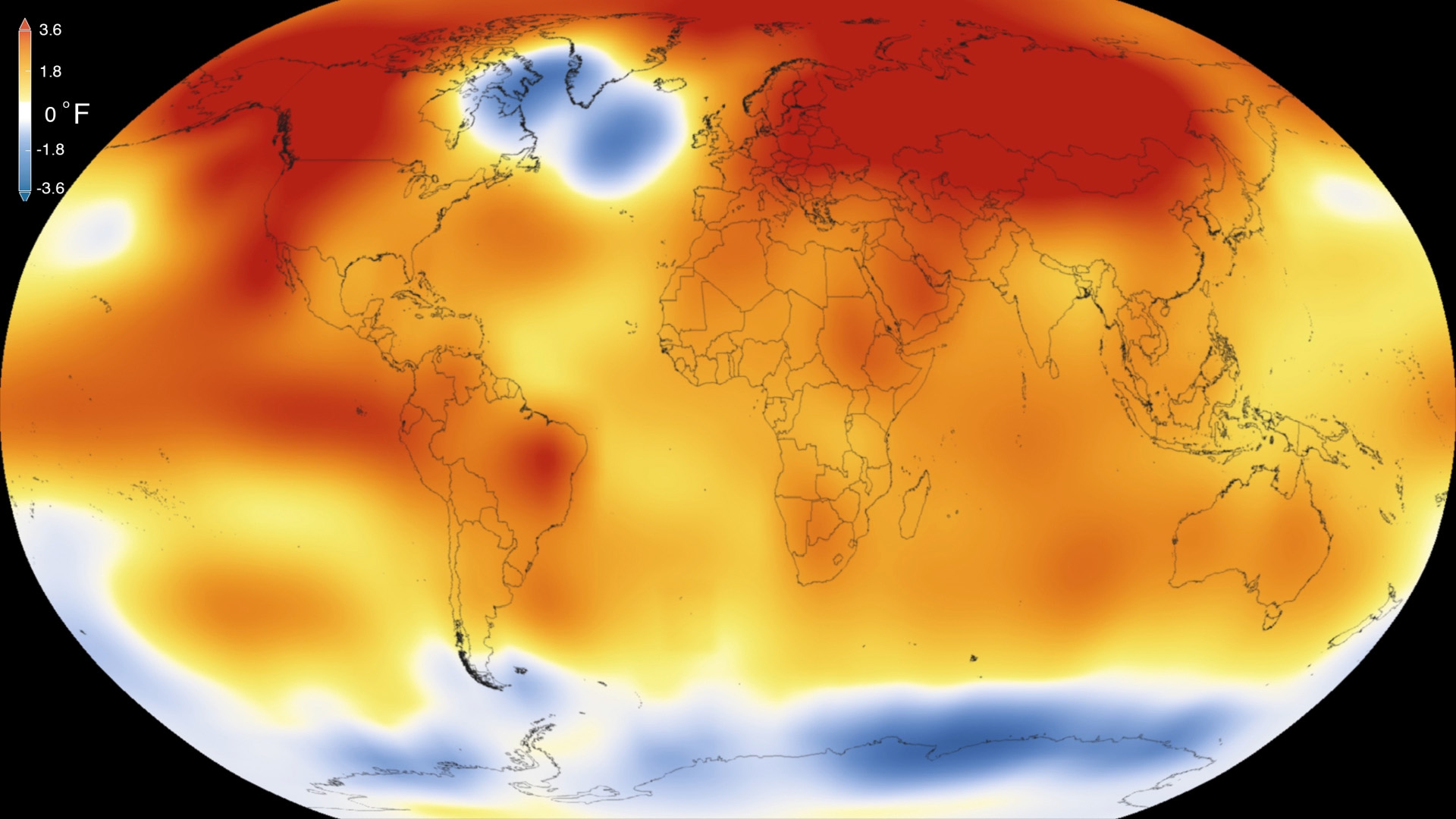
NASA, NOAA Analyses Reveal Record-Shattering Global Warm Temperatures in 2015. 2015 was the warmest year since modern record-keeping began in 1880, according to a new analysis by NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies. The record-breaking year continues a long-term warming trend — 15 of the 16 warmest years on record have now occurred since 2001
According to the 2015 Lancet Commission on Health and Climate Change, the threat to human health from climate change is so great that it could undermine the last 50 years of gains in development and global health.
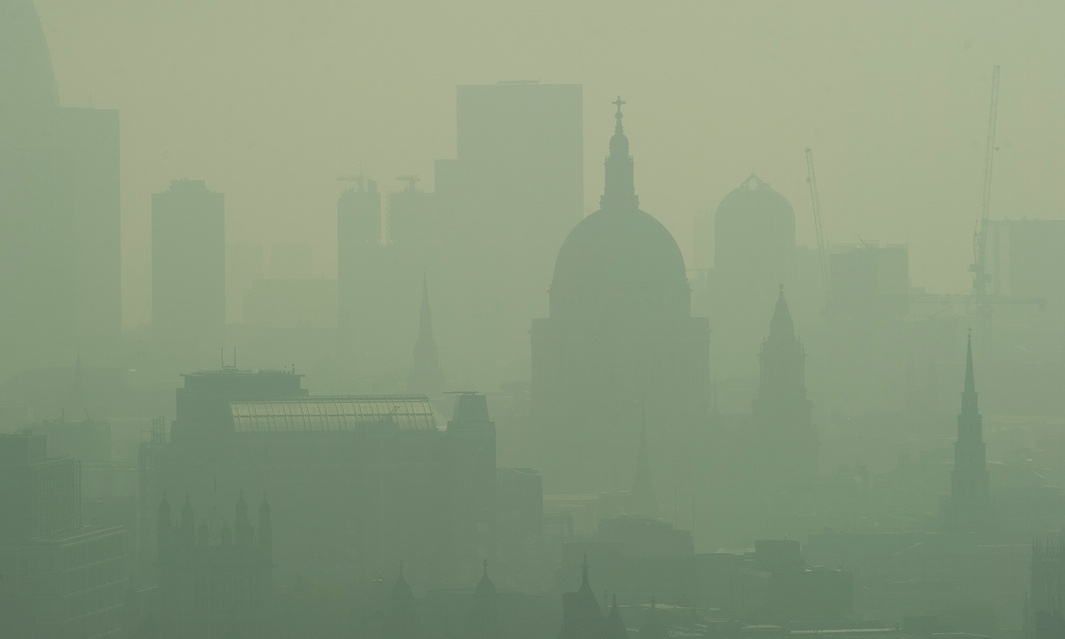
Extreme weather events such as floods and heat waves bring rising risks of infectious diseases, poor nutrition and stress, the specialists said, while polluted cities where people work long hours and have no time or space to walk, cycle or relax are bad for the heart as well as respiratory and mental health.
Almost 200 countries have set a 2 degrees C global average temperature rise above pre-industrial times as a ceiling to limit climate change, but scientists say the current trajectory could lead to around a 4 degrees C rise in average temperatures, risking droughts, floods, storms and rising sea levels.
“That has very serious and potentially catastrophic effects for human health and human survival,” said Anthony Costello, director of University College London’s (UCL) Institute for Global Health, who co-led the report. “We see climate change as a major health issue, and that’s often neglected in policy debates,” he told reporters at a briefing in London. The report, commissioned and published by The Lancet medical journal, was compiled by a panel of specialists including European and Chinese climate scientists and geographers, social, environmental and energy scientists, biodiversity experts and health professionals.
It said that because responses to mitigate climate change have direct and indirect health benefits – from reducing air pollution to improving diet – a concerted effort would also provide a great opportunity to improve global health.
The report said direct health impacts of climate change come from more frequent and intense extreme weather events, while indirect impacts come from changes in infectious disease patterns, air pollution, food insecurity and malnutrition, displacement and conflicts.
“Climate Change is a medical emergency,” said Hugh Montgomery, director of UCL’s institute for human health and performance and a co-author on the report. “It demands an emergency response using technologies available right now.”
The panel said there were already numerous ways to bring about immediate health gains with action on climate change.
Burning fewer fossil fuels reduces respiratory diseases, for example, and getting people walking and cycling more cuts pollution, road accidents and rates of obesity, diabetes, heart disease and stroke.
Cardiovascular disease is the world’s number one killer, leading to some 17 million deaths a year, according to World Health Organization data.
“There’s a big (energy) saving in people using calories to get around, and there are some immediate gains from more active lifestyles,” Montgomery said.
The commission also recommended the creation of a new global independent body with the task of monitoring climate change and global health. This coalition would report every two years on the health effects of climate change, track the progress of policies designed to mitigate climate change and make new suggestions on how to further adapt to climate change and implement low-carbon, sustainable health systems.
SOURCE: The Lancet, news release, June 22, 2015